Is your thyroid healthy? How to test your thyroid.
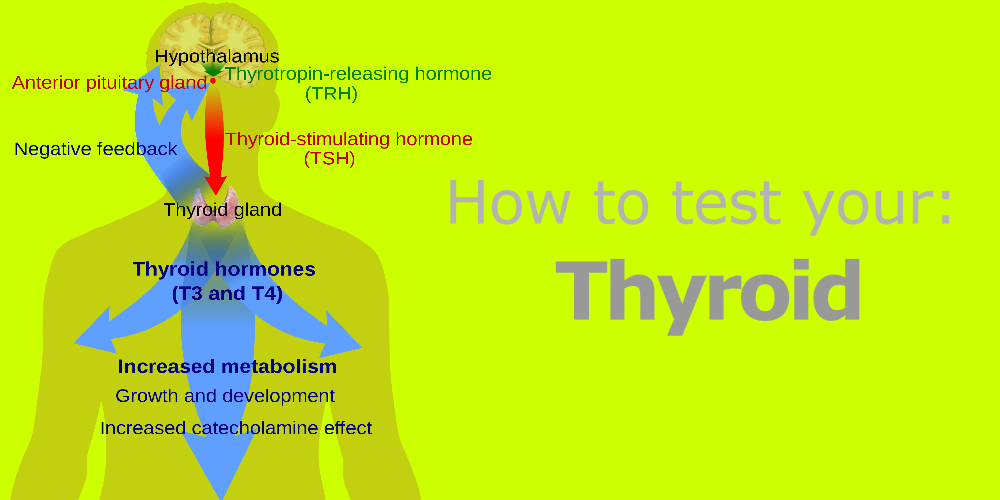
Your thyroid is the butterfly shape gland that sits at the front of the neck below the muscle laters. The thyroid makes thyroid hormone which regulates the metabolism of every cell in your body. This might sound simple and powerful yet your thyroid hormones are so interconnected that making sure your thyroid is functioning properly is important to ensure other systems are working as well.
Here is an overview on the thyroid hormones:
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) – This is the hormone your brain (the pituitary gland) sends out telling your thyroid gland to produce more thyroid hormone. If there is too little thyroid hormone, your brain will send out more TSH, and if there is too much thyroid hormone, it will release less TSH. In sum, TSH goes up when thyroid function is low.
Optimal Range: 1.3 -2.5
T3 – Most Important. TSH acts on the thyroid with then produces T4 and T3. This is the most active form of thyroid hormone. With birth control there can be low T3 uptake (birth control causes a conversion problem for T4 to T3
Optimal Range: 100-170
T4 – T4 is produced in significantly greater quantities and gets converted to T3 which is more biologically active.. You are looking at T3 and T4 together to see if there is a conversion issue.
Optimal Range: 6.0-12
T3Uptake – Here you would be looking for low uptake. Birth control can cause low uptake. And low zinc, selenium,and low iodien can cause a T4 –> T3 conversion problem.
Optimal Range: 27-37
TPO (antibodies) – This is important to look at to see if there is an autoimmune issue.
Optimal Range: 6-13
Free T4 – This is the form of thyroid hormone sent out by the thyroid gland to regulate metabolism in the rest of the body. Only 2% of this hormone gets absorbed so it is a way to show the function/biological activity of the thyroid more than anything. Optimal Range: 1.0-1.5
Free T3 – Most Important along with T3. A more potent form of thyroid hormone. Tissues that receive T4 will convert it to T3 which is 300% more active than T4. The reason T4 is sent out instead of T3 by the thyroid gland is because T3 only has a half life of 2.5 days where has T4 has a half life of 6.5 days. One of the effects of T3 is: stimulates the breakdown of cholesterol and increases the number of LDL receptors, thereby increasing the rate of lipolysis.
Optimal Range: 3-4
Reverse T3 (rT3) – Tissues that receive T4 can also convert it to rT3, an inactive form of T3. With stress your body will shunt T3 into Reverse T3. This occurs in certain conditions in which your body tries to conserve energy by slowing down metabolism such as fasting, low carbohydrate intake, physical or emotional stress, illnesses, surgery etc. Thus, under these conditions, not only will you have less overall T3 floating around, but rT3 can block T3 receptors so that the T3 you have left are even less effective.
Optimal Range: 11-23
Note: Rages come from Dr. Justin Marchegiani at Justinhealth who explains that the ranges most lab test fall under are not optimal ranges. The “normal” ranges keep getting wider and wider as people start getting sicker and sicker.
Symptoms of Low Thyroid:
- Fatigue
- Increased sensitivity to cold
- Constipation
- Dry skin
- Unexplained weight gain
- Puffy face
- Hoarseness
- Muscle weakness
- Elevated blood cholesterol level
- Muscle aches, tenderness and stiffness
- Pain, stiffness or swelling in your joints
- Heavier than normal or irregular menstrual periods
- Thinning hair
- Slowed heart rate
- Depression
- Impaired memory
Activities that Damage Your Thyroid:
- Chronic Stress
- Birth control for extended periods of time
- Endurance Excercise
- Back to back days of Cross Fit or HIIT
- No recovery days
- Don’t eat enough leafy greens
- Don’t eat enought healthy proteins pasture eggs, wild caught salmon, grass fed beef
- Don’t eat enough iodine (get it naturally from seaweed, nori)
Leave a Reply